|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
When people hear “blockchain”, they immediately think we’re going to start talking about cryptocurrency or bitcoin, but blockchain technology is so much more.
Gartner lists blockchain as one of the top strategic technology trends for 2019 saying:
“Blockchain could potentially lower costs, reduce transaction settlement times and improve cash flow.”
For businesses, even those outside of the financial industry, blockchain technology has tremendous potential.
But, let’s not get ahead of ourselves: The first step is understanding blockchain technology and how it works.
Blockchain Explained
Think of blockchain like an old-style accounting ledger. In a ledger, entries made to record a deposit or a withdrawal are inked on separate lines to amend the data in the ledger. New transactions never edit or erase earlier entries.
Blockchain works in much the same way. Data is entered into the first block and changes or updates are recorded in separate blocks.
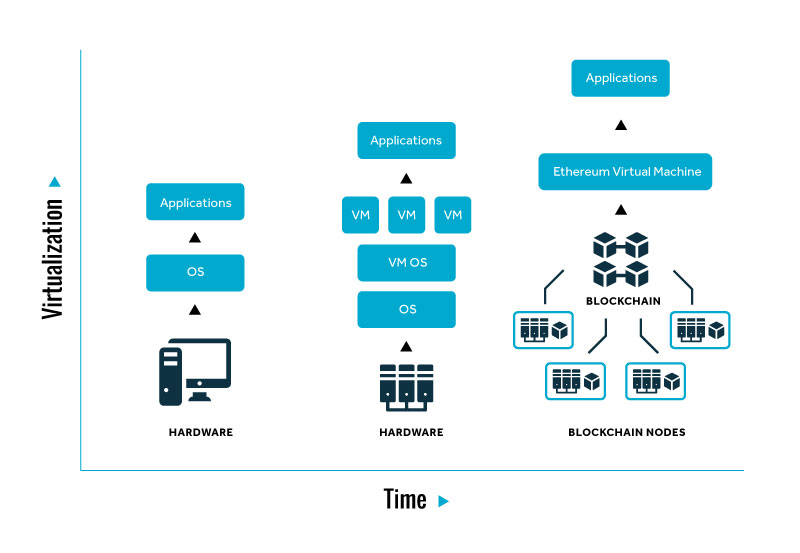
It might be tempting to think that blockchain is a glorified database using a hyped-up new technology. It’s not. It’s much different.
In a database, you can upload new data, change entries or delete data, adhering to permissions and security settings (unless you’ve hacked in). In a blockchain, once the data is recorded, that block is locked and the data entered can never be changed, it can only be amended, just like the pen and paper accounting ledger.
Blockchain Security
A blockchain is created using cryptographic tools such as Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) and hashing algorithms. PKI tools allow transactions in a block to be digitally signed. Hashing algorithms ensure data integrity.
Very simplistically, cryptographic hashing means the data is run through an algorithm that assigns a unique signature ID to the data. If data is digitally signed using a hash, the integrity of the data can be verified by running the data through the same hash. If the resulting hash is the same as the original, the data has not been modified.
A block contains a set of data and when a new block is added to the chain, the hash of that block is added to the subsequent block and so on. The blockchain itself is distributed across thousands or millions of computers around the world.

Why is this important?
If someone tries to change a block, the signature ID of the block will change instantly, and all subsequent blocks will be invalid and show errors. You can’t make even a small change (like adding a space or a comma) without invalidating all the subsequent blocks in the chain.
Blockchain Advantages
When it comes to recording and securing data, blockchain technology offers a few important advantages:
- Immutable – data can’t be altered by anyone. You can amend the data, you can add data, but you can never go back and change it and the history of all amendments is logged.
- Decentralized & distributed – there is not one central organization controlling the data (who by extension could change it). The blockchain system is a network of blockchains distributed across the world which offers built in redundancy.
- Transparent – all parties to a blockchain can verify the data’s accuracy and review transactions from start to finish with confidence the information hasn’t been modified.
While many people might be familiar with a public blockchain (like the public distributed network that supports cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin), you might not realize that businesses can deploy a blockchain on a private network to limit and secure access, creating a private blockchain.
Blockchain In-Practice
Does Blockchain technology have real business applications beyond bitcoin or the financial sector? You bet it does.
We used a blockchain solution for a client to securely log and communicate flight data with Transport Canada.
We built a private blockchain network in Microsoft Azure using Ethereum to maintain a complete, immutable log of every flight including date, location, weather conditions, take off weight, package details, routing and more.
If Transport Canada wants to see data related to a specific flight as part of an audit or for an investigation, they can access the logs with confidence that the information is an accurate, unmodified reporting of all the flight details.
Opportunities for Blockchain Solutions
With its roots in cryptocurrency, it’s not surprising people point to the financial sector for examples of places that blockchain could be valuable, but there are many more potential applications.

- Health care – securing health and medical records and reducing the potential for fraud.
- Legal industry – for critical documents like wills, powers of attorney and corporate records, not to mention the creation of smart contracts.
- Real estate – when recording land transfers and real estate transactions while reducing the potential for fraudulent sales.
- Supply chain – Walmart is already using blockchain to track some products back to their manufacturing roots, and UPS and FedEx have started using blockchain in their operations.
- Raising capital – Initial coin offerings or ICOs are raising money for businesses and being used to support crowdfunding projects.
- Education – student IDs, transcripts, test result records and more could benefit from blockchain’s immutability and security.
In a world where fraud and security incidents are becoming more and more commonplace, blockchain is an excellent technology that can provide businesses with a very secure way to work with customers, suppliers and partners.
Definitions
Blockchain: An incorruptible digital ledger of transactions or data.
Cryptocurrency: Digital or virtual currency that uses cryptography for security.
Bitcoin: One type of cryptocurrency and the most common.
Cryptographic Hashing: A mathematical algorithm that maps data to create a fixed value string (such as a 32-character number) as a signature ID. Cannot be reverse engineered to get the original data back.
Digital Signature: A method to ensure authenticity and integrity of data. Provides assurance that a data has been authenticated and has not been changed.
Public Key Infrastructure: Info encrypted with a private key can only be decrypted with a corresponding public key and vice versa facilitating the secure, authenticated electronic transfer of information.
Ethereum: Ethereum is a decentralized computing platform that runs applications on a custom built blockchain.